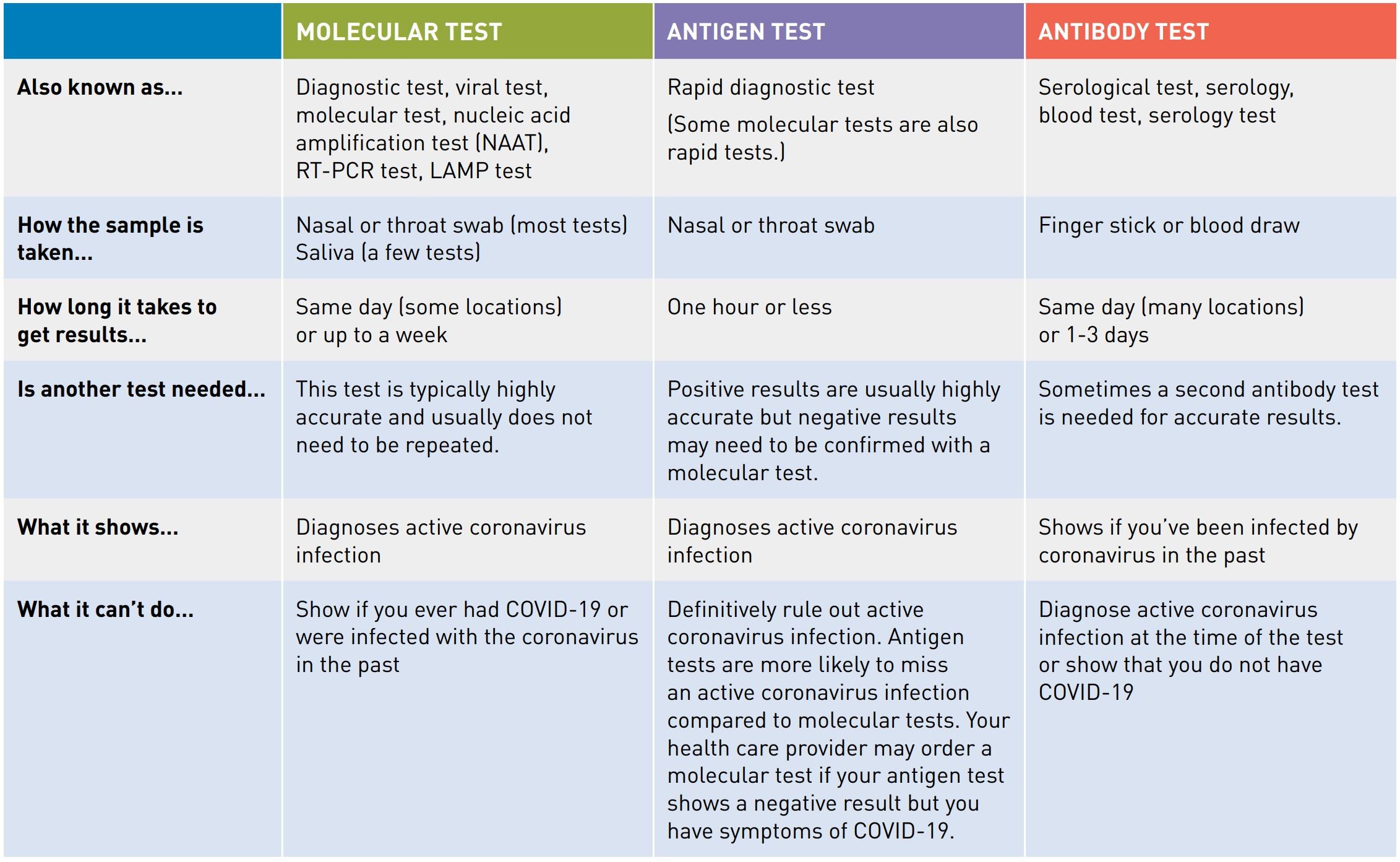
We take a look at the three main COVID-19 testing methods.
SARS-CoV-2, a strand of the coronavirus which causes COVID-19, has taken the world by storm. Many have lost their jobs, unable to visit loved ones, and in some cases, left to quarantine from their homes.
Recently, more and more coronavirus tests are being made available to the general public. The more tests made available, the more excellent confident public health can be, while also analyzing the full extent and impact the virus has had on the nation.
However, how do you know which test is more suitable for you? Should you spend money on an antibody test, or should you route a COVID-19 rapid antigen swab test? To help you answer these questions, and more, this article will discuss the three main COVID-19 testing methods: molecular testing, antibody tests, and antigen tests.
Let’s begin.
Molecular testing: RT-PCR
RT-PCR testing is currently the most popular method of testing available. The RT-PCR test is the gold-standard for COVID-19 diagnosis, detecting whether an individual currently has the virus in upper respiratory samples, or called an active infection.
RT-PCR tests detect the virus’s genetic information, the presence of a specific RNA segment instead of a viral protein (the antigens) or the body’s response (the antibodies). The RT-PCR test is usually taken upper respiratory samples via a nasal or throat swab, with results later revealed by a testing laboratory. If urgent, results can be accessed (if the facilities are available) within a few hours.
However, RT-PCR tests are almost 100% accurate in detecting active infections, unless a patient is in the late infection stage, during which the SARS-CoV-2 level drops significantly in upper respiratory.
Pros:
- The gold-standard for COVID-19 detection, high sensitivity
- Reliable reagents and raw materials
- Helps to decide who should be in quarantine
Cons:
- Expensive
- Requires a laboratory
- It may take days to receive your results
Antibody testing
COVID-19 antibodies develop in your blood one to three weeks after infection. Antibody testing is used extensively to assess what percentage of the population has already been infected, also helping us determine who needs to self isolate, e.g., who has the infected individual been in contact with recently.
Unlike RT-PCR and antigen tests, antibody tests don’t have much use within the initial testing phase – there is greater scope for error since antibodies do not develop in the human body during an active infection phase or an early stage of infection. For this reason, antibody tests are rarely used as the first point of contact to detect whether or not an individual has COVID-19.
Pros:
- Can determine whether one has been infected
- Identify later stage infection as an aid to RT-PCR
- Potentially help with checking vaccine status
Cons:
- Does not detect active infection
- Low accuracy
COVID-19 antigen rapid swab test kit
Another popular testing method for the deadly virus is a lateral flow COVID-19 antigen rapid test kit. SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests detect specific proteins associated with the virus. This method is simple, providing accurate results as to whether an individual has the virus or suffers an active infection. Much like molecular testing, samples are also taken from upper respiratory via throat or nasal swabs, usually performed by a healthcare professional. The US FDA has opened up a template for the application of Over-The-Counter purpose.
Unlike PCR tests, COVID-19 antigen rapid test kit results are produced within 10-20 minutes, which provides ease of mind and increased safety among others, for example, while at home (OTC). This form of testing is also less expensive than PCR tests, making them great for testing a large number of people in a small timeframe.
A positive antigen test is recognized as an accurate indication of the virus, especially during the first five days after symptoms onset. However, this test’s accuracy highly depends on the inclusion criteria of a clinical evaluation since the number of viral antigen drops over time.
Pros:
- Less expensive than other testing methods
- Widely accessible and easy to operate
- High specificity, low false positive rate
- 15-minute rapid detection
Cons:
- Not as accurate as RT-PCR tests
To conclude
Coronavirus tests are slowly becoming more and more accessible to the general population. However, knowing which test is best can be difficult, especially if you’ve never heard of them before.
The COVID-19 antigen rapid test kit is one of the most effective, quick, and accessible testing methods currently available when medical resources are limited, and RT-PCR tests cannot generate results promptly. Unlike antibody tests, the antigen swab tests are much more accurate, which can detect active SARS-CoV-2 infection.